What is Gravure Printing?
Several methods stand out in the world of printing and packaging for their ability to produce high-quality, vibrant, and detailed images. Gravure printing, also known as rotogravure, holds a special place for its precision, efficiency, and versatility. This blog post will delve into the intricacies of gravure printing, exploring its process, advantages, applications, and how it compares to other printing methods.
Understanding Gravure Printing
Gravure printing is an intaglio printing process that involves engraving an image onto an image carrier. In gravure printing, the picture is engraved onto a cylinder, making it one of the few printing techniques that directly use a cylindrical image carrier. This unique aspect of gravure printing allows for the consistent, high-quality reproduction of images, making it ideal for various applications, from packaging and magazines to wallpaper and furniture laminates.
The Process of Gravure Printing
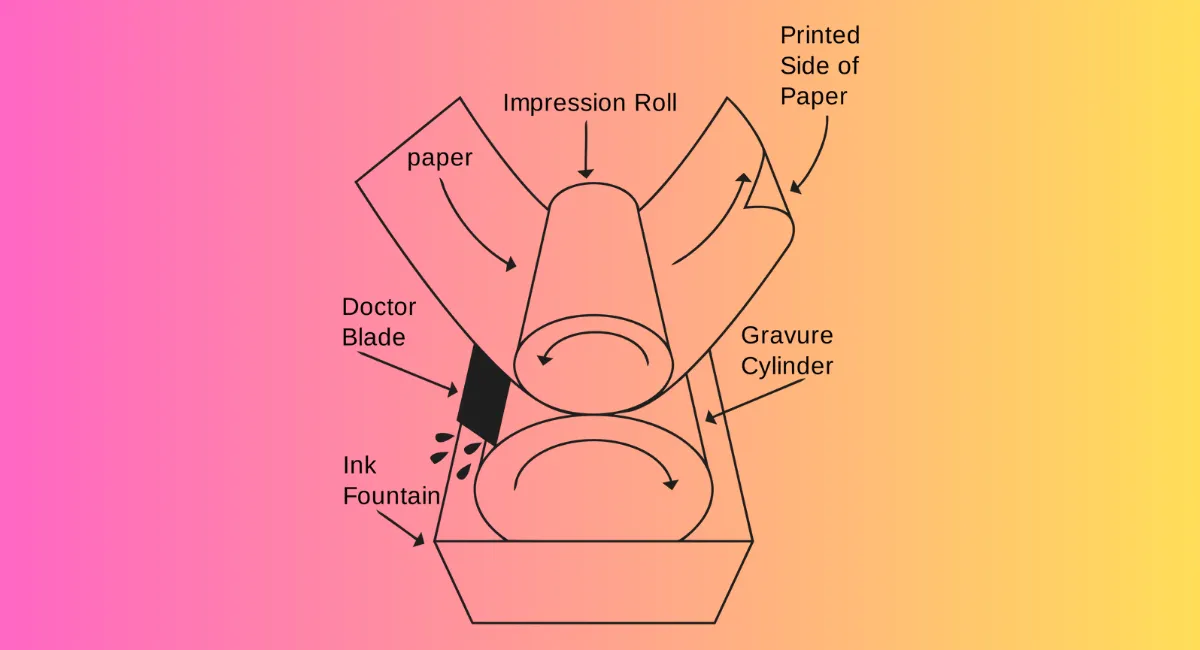
The gravure printing process is both fascinating and complex, involving several key steps:
- Engraving the Image: The first step in gravure printing is creating the image cylinder. This involves carving the image onto a cylinder, traditionally done mechanically but now often achieved through laser etching. The depth and size of the cells are varied to modulate the amount of Ink each cell holds, thus controlling the shading and detail of the printed image.
- Inking the Cylinder: Once the cylinder is engraved, it is coated with Ink. The entire surface gets covered, ensuring that Ink fills all the engraved cells.
- Wiping Excess Ink: After inking, the non-image areas are cleaned of excess Ink using a doctor’s blade. This step is crucial as it ensures that Ink remains only in the engraved cells.
- Transferring Ink to the Substrate: The inked cylinder is pressed against the substrate (paper, plastic, etc.), moving the Ink from the cells onto the material. Due to high-pressure rollers, the Ink from the deep cells is efficiently transferred to the substrate, creating a high-definition image.
- Drying the Ink: Finally, the printed material is passed through a dryer to cure the Ink, ensuring the print is set and resistant to smudging or fading.
Advantages of Gravure Printing
Gravure printing offers several distinct advantages:
- High Quality and Durability: It produces prints of exceptional quality and durability, with rich colors and sharp details.
- Consistency: The method ensures consistent results across long runs, making it ideal for large-scale productions.
- Versatility: Gravure printing can be used on various materials, including paper, cardboard, plastic, and metal foils.
- Efficiency: Although the initial setup costs can be high due to cylinder engraving, the process is highly efficient for long runs, making it cost-effective over time.
Applications of Gravure Printing
Gravure printing’s versatility and high-quality output have made it a preferred choice in various industries. Some typical applications include:
- Packaging: From food and beverage to cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, gravure printing is widely used to produce vibrant, durable packaging.
- Publication: High-end magazines, catalogs, and brochures benefit from the rich colors and fine details gravure printing can achieve.
- Decorative Printing: Gravure printing is often used for high-quality finishes and durability in wallpaper, furniture laminates, and other decorative items.
Comparing Gravure Printing with Other Methods
While gravure printing offers many benefits, comparing it with other printing methods like offset and digital printing is essential to understanding its unique place in the printing landscape. Offset printing is another high-quality method but is generally more cost-effective for medium to large runs and less for the very high volumes or the extremely high-resolution needs met by gravure printing. Digital printing, on the other hand, offers more flexibility for short runs and variable data printing but cannot match the quality and efficiency of gravure printing for large-scale productions.
Conclusion
Gravure printing stands out in print for its unmatched quality, durability, and efficiency, especially in high-volume productions. Its ability to produce vivid, detailed images on various substrates makes it a go-to choice for high-end publications, quality packaging, and decorative applications. Despite the initial setup costs, the long-term benefits of gravure printing—consistency, quality, and cost-effectiveness—make it a valuable printing technique for businesses and designers alike. As technology advances, gravure printing continues to evolve, further enhancing its efficiency and expanding its applications, ensuring its place in the future of printing and packaging.



