What is GSM? Paper Weight, Fabric Weight, and Custom Printing Explained
In packaging, presentation, and printing, the term “GSM” stands out as a fundamental concept that professionals and consumers should understand. GSM stands for Grams per Square Meter and is a unit of measurement used to define the weight and thickness of paper and fabric materials. It is crucial in determining the quality, durability, and final appearance of printed products and packaging solutions. This blog will dive deep into what GSM means for paper and fabric weight and how it influences custom printing projects.
Understanding GSM in PaperWeight
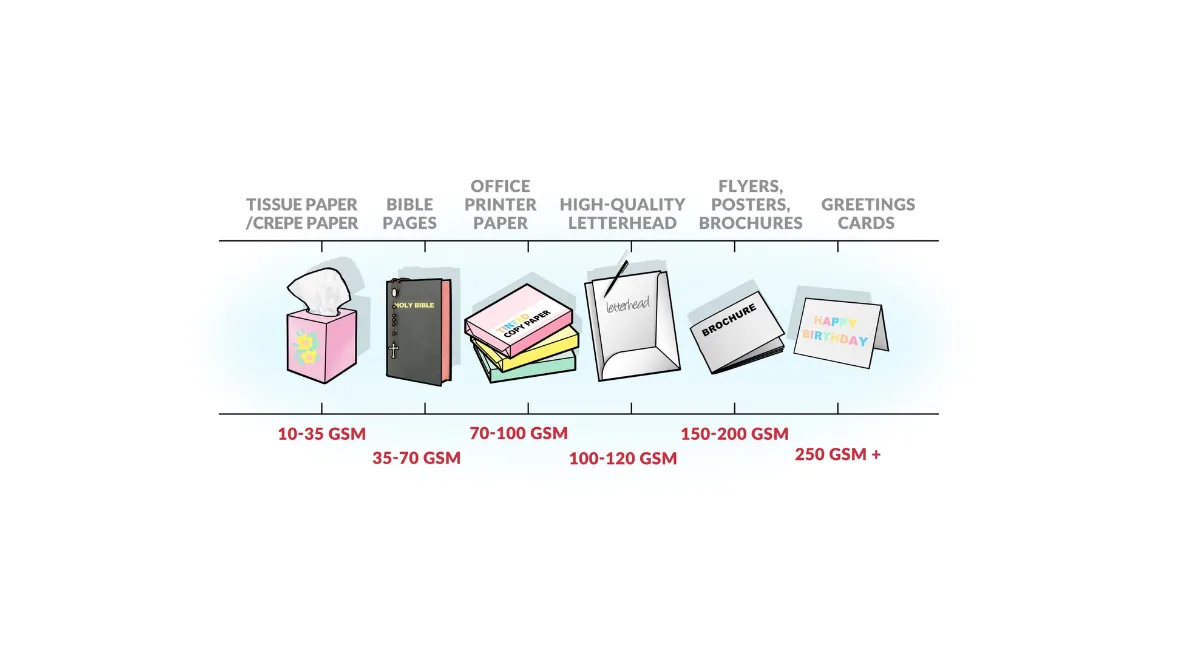
When it comes to paper, GSM is a critical factor that influences not only the feel and sturdiness of the paper but also how it will handle printing and ink absorption. Papers with higher GSM values are thicker and heavier, offering a more luxurious and substantial feel. This makes them ideal for high-end printing projects such as business cards, invitation cards, and brochures. On the other hand, lower GSM papers are lighter and more flexible, suitable for everyday use like newspapers and notebooks.
The choice of paper GSM affects the overall quality and perception of the printed material. For instance, 90 GSM paper is commonly used for letterheads and standard office documents, balancing quality and cost. Meanwhile, a 300 GSM paper would be selected for a premium business card, ensuring durability and a premium feel.
The Role of GSM in Fabric Weight
In the textile industry, GSM is a critical indicator of the weight and density of the fabric, impacting its texture, strength, and drapability. Higher GSM fabrics are thicker, more durable, and often warmer, making them perfect for winter clothing, upholstery, and heavy curtains. Conversely, fabrics with a lower GSM are lighter and more breathable, ideal for summer apparel, linens, and lightweight drapes.
The GSM of fabric affects not only the physical characteristics of the product but also its application and suitability for specific print methods. For example, a low GSM fabric might be excellent for digital printing techniques that require a delicate touch. In contrast, a heavier fabric might be more suited to screen printing or embroidery.
GSM’s Impact on Custom Printing
When it comes to custom printing, understanding the importance of GSM is paramount for achieving desired outcomes. The weight of the paper or fabric not only influences the look and feel of the finished product but also how well it will accept and display printed designs.
Paper Custom Printing
In custom paper printing, the choice of GSM can significantly affect printability, colour saturation, and image clarity. Heavier papers can absorb more ink without warping or bleeding, essential for vibrant and detailed prints. However, using too thick paper for your printer can lead to issues like paper jams and poor ink transfer, underscoring the importance of matching the GSM to the printing method and equipment.
Fabric Custom Printing
For custom fabric printing, the GSM impacts the printing technique used and the final appearance of the print. High GSM fabrics may require more robust printing techniques like screen printing to ensure the ink penetrates the thick material. On the other hand, lower GSM fabrics are well-suited for techniques like dye sublimation, which can create vivid colours and sharp details on lightweight textiles.
Conclusion
Understanding GSM is crucial for anyone selecting paper and fabric for printing and packaging purposes. It determines the material’s quality, durability, and suitability for various printing techniques and end-uses. Whether you’re a designer, printer, or consumer, taking GSM into account will help ensure that your final product meets your expectations in terms of both aesthetics and functionality. By making informed decisions about GSM, you can elevate the quality of your printed materials and packaging, creating a lasting impression on your audience.



